How Autoimmune Leaky Gut Causes Disease
Did you know that your gut health is more than just about digestion? It’s the key to unlocking the mysteries of autoimmunity. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of autoimmune leaky gut, explore the role of gut microbiota in autoimmune diseases, and learn about different strategies that can help improve gut health and reduce autoimmune symptoms. Get ready to embark on a journey that could change the way you think about your health forever!
Key Takeaways
-
Leaky gut syndrome can lead to autoimmune disorders and inflammation.
-
Dietary, environmental and medication factors affect intestinal permeability.
-
Take control of your health by incorporating dietary modifications, stress management techniques & functional medicine approaches for improved gut health & reduced symptoms of autoimmune diseases!
Understanding Autoimmune Leaky Gut
Imagine your gut as a fortress, protecting your body from harmful bacteria, toxins, and viruses. When the walls of this fortress are strong, these harmful substances are kept at bay. But when the walls are weakened, these invaders can infiltrate the body, triggering a cascade of events that can ultimately lead to autoimmune diseases.
The weakening of these walls can be attributed to a condition called leaky gut syndrome, or increased intestinal permeability. Leaky gut syndrome is a condition where the gut barrier, which is made up of a single layer of cells called enterocytes, becomes compromised, allowing harmful substances to pass through into the bloodstream. This can lead to an overactive immune response, inflammation, and eventually, autoimmune disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease (including ulcerative colitis), celiac disease, and multiple sclerosis.
A significant 80% of immune cells are situated within the gastrointestinal tract, indicating a close link between gut health and immune function.
The Role of Intestinal Barrier
Consider the intestinal barrier as your body’s security system, filtering out harmful substances while letting beneficial nutrients pass. When functioning properly, it plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and preventing autoimmune leaky gut. The integrity of this barrier is maintained by the tight junctions between enterocytes, which act as gatekeepers, ensuring only necessary nutrients can pass through while keeping harmful substances at bay.
Yet, factors such as dietary habits, environmental toxins, and persistent stress can disrupt these tight junctions, allowing harmful substances to infiltrate the bloodstream and increasing intestinal permeability. This breakdown of the intestinal barrier can trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation and potentially the development of autoimmune diseases.
Causes of Increased Intestinal Permeability
There are several factors that can contribute to increased intestinal permeability, also known as leaky gut. These factors include:
-
Dietary factors such as gluten and other inflammatory foods
-
Gut infections like small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), Candida, and parasites
-
Environmental toxins
-
Stress
-
Certain medications
All of these factors can contribute to the weakening of the gut lining.
Gastrointestinal diseases like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Crohn’s disease, and celiac disease can also result in increased intestinal permeability. Other conditions like food allergies, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and critical illnesses can play a role in increasing intestinal permeability as well.
Recognizing and addressing these factors is key to preserving a healthy gut and thwarting the onset of autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune Diseases Linked to Leaky Gut
Leaky gut has been linked to a number of autoimmune diseases, such as:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
-
Celiac disease
-
Autoimmune hepatitis
-
Type 1 diabetes
-
Multiple sclerosis
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
This is because when the intestinal barrier is compromised, harmful substances can enter the bloodstream, causing the immune system to mistakenly attack the body’s own tissues, leading to autoimmune disorders.
A paper was recently published in Frontiers in Immunology which aimed at reviewing the scientific evidence behind leaky gut syndrome as a potential cause of autoimmune diseases. The paper concluded that there is sufficient proof to establish a direct relation between the two conditions. Understanding the link between leaky gut and autoimmune diseases allows us to emphasize the importance of gut health and investigate potential treatments for these conditions.
Impact of Gut Microbiota on Autoimmune Diseases
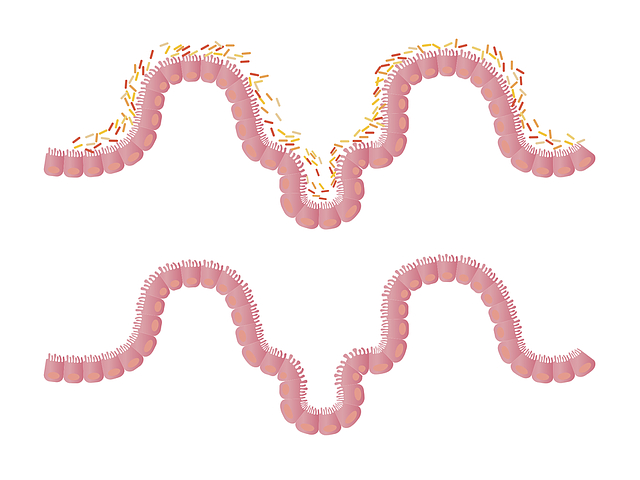
The gut microbiota, which is the collection of trillions of microorganisms, including gut bacteria, living within our gastrointestinal tract, plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. It is responsible for regulating our immune system, maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier, and producing essential nutrients and signaling molecules in the digestive system.
However, when the balance of the gut microbiota is disturbed, it can contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases. An altered gut microbiota can lead to increased intestinal permeability, potentially triggering an immune response that can result in the development of autoimmune diseases. The cause of this can be attributed to a range of factors, such as diet, stress, and environmental toxins.
Gaining insight into the relationship between gut microbiota and autoimmune diseases can guide us towards potential interventions to restore balance and enhance immune health.
Beneficial Bacteria and Immune Function
Beneficial bacteria are essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. They help regulate the immune response, preventing over-activation of the immune system and protecting against pathogens. Additionally, they help maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier, which is crucial for preventing autoimmune diseases.
Incorporating probiotic-rich foods, prebiotic-rich foods, and nourishing bone broth into your diet can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, which in turn can help reduce inflammation, enhance digestion, and balance the gut microbiome. Supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria enables you to actively enhance your gut health and safeguard against autoimmune diseases.
Altered Gut Microbiota and Autoimmune Pathogenesis
Altered gut microbiota, or dysbiosis, can disturb the balance between the immune system and the microbiota, resulting in immune dysregulation and the emergence of autoimmune diseases. This disruption can occur when the composition of the gut microbiota is changed due to factors such as diet, stress, and environmental toxins. As a result, the intestinal barrier function and immune cell activity can become impaired, leading to the development of autoimmune diseases.
Fortunately, addressing the root causes of dysbiosis and rebalancing the gut microbiota can potentially mitigate inflammation, enhance gut health, and restore immune system balance, thus paving the way to regain health and well-being.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation as a Potential Treatment
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) is a promising treatment option for autoimmune diseases that involves transferring fecal matter from a healthy donor into the intestinal tract of the recipient. By introducing healthy bacteria and restoring the balance of the gut microbiota, FMT has been shown to:
-
Reduce inflammation
-
Improve gut health
-
Potentially alleviate symptoms of autoimmune diseases such as celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
While FMT is generally deemed safe, discussing potential risks with a healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure is highly recommended. By exploring this novel treatment option, we can potentially open up a new avenue for reducing the incidence of autoimmune diseases and improving overall gut health.
Strategies for Improving Gut Health and Reducing Autoimmune Symptoms

Taking control of your gut health and reducing autoimmune symptoms involves a holistic approach that includes dietary modifications, stress management techniques, and functional medicine approaches. Start healing your gut by adopting a combination of these strategies. You can improve your gut health and potentially reverse autoimmune leaky gut.
Keep in mind that each individual’s gut microbiota is unique, and a strategy effective for one person may not yield the same results for another. Therefore, it’s important to experiment with different strategies and work closely with a healthcare professional to find the best approach for your unique needs.
Dietary Modifications
Diet plays a crucial role in promoting gut health and managing autoimmune symptoms. Avoiding certain foods that can trigger inflammation and damage the gut lining is essential, while consuming certain foods that can help to heal the gut and reduce inflammation is highly beneficial.
To maintain gut health and manage autoimmune symptoms, it’s beneficial to incorporate whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts into your diet, while avoiding processed foods, refined sugars, gluten, dairy, and nightshade vegetables. Additionally, including probiotic-rich foods, prebiotic-rich foods, nourishing bone broth, and flavorful anti-inflammatory herbs and spices can help heal your gut and reduce inflammation.
Stress Management Techniques
Effective stress management plays a vital role in promoting gut health and mitigating autoimmune symptoms by helping to reduce inflammation, boost digestion, and maintain a balanced gut microbiome. Incorporating stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises into your daily routine can help you maintain a healthy gut and prevent the development of autoimmune diseases.
In addition to practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, it’s important to ensure you get adequate sleep, consume a balanced diet, and engage in regular physical activity to support your overall gut health. By adopting these habits, you’ll be better equipped to manage stress and maintain a healthy gut, reducing your risk of autoimmune diseases.
Functional Medicine Approaches
Functional medicine provides a distinctive approach to pinpointing and tackling the root causes of autoimmune leaky gut, including dietary habits, lifestyle factors, environmental toxins, and genetic susceptibilities. By tackling these root causes, functional medicine can help reduce inflammation, improve gut health, and restore balance to the immune system – giving you the best chance of restoring your health and wellbeing.
Some functional medicine approaches that can help improve gut health and reduce autoimmune symptoms include:
-
Taking probiotics
-
Taking prebiotics
-
Taking herbal supplements
-
Following a gut healing protocol
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can take control of your gut health and start feeling better.
Case Studies: Reversing Autoimmune Leaky Gut

There are many inspiring success stories of individuals who have been able to reverse autoimmune leaky gut through various interventions. These case studies demonstrate the power of taking control of your gut health and adopting a comprehensive approach to address the root causes of autoimmune diseases.
These real-life examples provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of diverse strategies and treatments in reversing autoimmune leaky gut, and serve as motivation to take proactive steps towards improving our own gut health.
Celiac Disease and Gluten-Free Diet
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Studies have shown that a gluten-free diet can be highly effective in managing celiac disease in up to 90% of cases. By eliminating gluten from the diet, the following benefits can be achieved:
-
Reduction of inflammation
-
Restoration of the integrity of the intestinal barrier
-
Healing of leaky gut
-
Improvement of overall health
Beyond its benefits for those with celiac disease, a gluten-free diet can also aid individuals with non-celiac gluten sensitivity or other autoimmune diseases by reducing inflammation and promoting gut healing.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gut Healing Protocol
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation and joint pain. One individual suffering from rheumatoid arthritis was able to reverse their symptoms by following a gut healing protocol that included dietary modifications, probiotic supplementation, and stress management techniques such as yoga and meditation. As a result, this person experienced significant improvements in their gut health and a reduction in their autoimmune symptoms.
This inspiring case underscores the efficacy of a comprehensive gut healing protocol in tackling the root causes of autoimmune diseases and enhancing overall health and well-being.
Multiple Sclerosis and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. Research has shown that fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) can potentially reduce inflammation and improve gut health in people with MS, offering a promising new treatment option.
One individual suffering from MS underwent FMT and experienced significant improvements in their gut health and a reduction in their autoimmune symptoms. This promising case exemplifies the potential of FMT in treating autoimmune diseases and enhancing overall gut health.
Summary
In conclusion, autoimmune leaky gut is a complex condition with far-reaching implications for our overall health and well-being. By understanding the role of the intestinal barrier, gut microbiota, and various treatment strategies, we can take control of our gut health and reduce our risk of developing autoimmune diseases. With a combination of dietary modifications, stress management techniques, functional medicine approaches, and revolutionary treatments like fecal microbiota transplantation, we can unlock the door to a healthier, happier life.
Check out our guide on how to heal your gut after food poisoning for more information. Also check out our prevention gut reactions blog post.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you treat autoimmune leaky gut?
To treat autoimmune leaky gut, focus on reducing inflammation through anti-inflammatory foods, increasing probiotics and prebiotics in your diet, supplementing with glutamine and reducing stress.
Additionally, it’s essential to treat the underlying conditions that cause leaky gut, such as IBD or celiac disease, which have been shown to repair the intestinal lining.
What are five signs of a leaky gut?
Leaky gut syndrome can manifest in five signs including nutritional deficiencies, persistent bloating, gas and diarrhea, immune system problems, mood challenges, and skin issues.
What are the physical symptoms of leaky gut?
Leaky gut can cause a variety of physical symptoms, such as bloating, diarrhoea, gas, IBS, headaches, skin issues, joint pain, fatigue and mood imbalances.
Food sensitivities, nutritional deficiencies, confusion and difficulty concentrating are also potential signs of this medical condition.
What diseases are associated with leaky gut syndrome?
Leaky gut syndrome is associated with inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, heart diseases, obesity, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and celiac disease.
It may also be triggered by other gut health issues such as food allergies, medication overuse, chemotherapy or chronic stress.
What is the relationship between leaky gut and autoimmune diseases?
Leaky gut is a condition that compromises the gut barrier, resulting in an overactive immune response and inflammation which can cause autoimmune disorders.
